The Social Impact Partnership Act
With tighter local and federal budgets, how can government more effectively innovate to achieve the public outcomes that Americans desire? One growing trend, both nationally and internationally, is social impact bonds (SIBs). Recently, Congressmen John Delaney and Todd Young, in partnership with America Forward, hosted a briefing on Capitol Hill releasing updates to the Social Impact Partnership (SIP) Act that expands support for SIBs at the federal level. Congressmen Young and Delaney, along with a bipartisan group of co-sponsors, introduced the SIP Act in the House on March 4, 2015 (similar legislation was introduced in the Senate on April 27, 2015, with sponsorship from Senator Orin Hatch). The SIP Act is intended to create federal-level support to help city and state governments leverage SIBs as a way to tackle local community problems with greater efficiency and accountability.
During the briefing, Brian Beachkofski, senior director at Third Sector Capital Partners; Jeff Shumway, vice president of advisory services at Social Finance, Inc.; and Jeremy Keele, executive director of the Policy Innovation Lab at the University of Utah, highlighted a number of SIBs-based projects currently being constructed in cities such as Salt Lake City, Boston, Chicago and Washington, DC.
How SIBs Function
SIBs, despite the name, are not actually bonds. Originally introduced in the United Kingdom, they are a new method of funding social services in a way that promotes outcomes over the number of services provided. One of the primary benefits of SIBs is the increase in efficiencies through private-sector capital and insights that allow government to identify what works before deploying tax dollars on an intervention (full definition). Other benefits to SIBs are the potential to fill certain social gaps, promotion of bipartisan cooperation within government and the opportunity to put tax dollars to work more effectively. (Watch Congressman Delaney’s TEDx Pennsylvania Avenue talk on SIBs.)
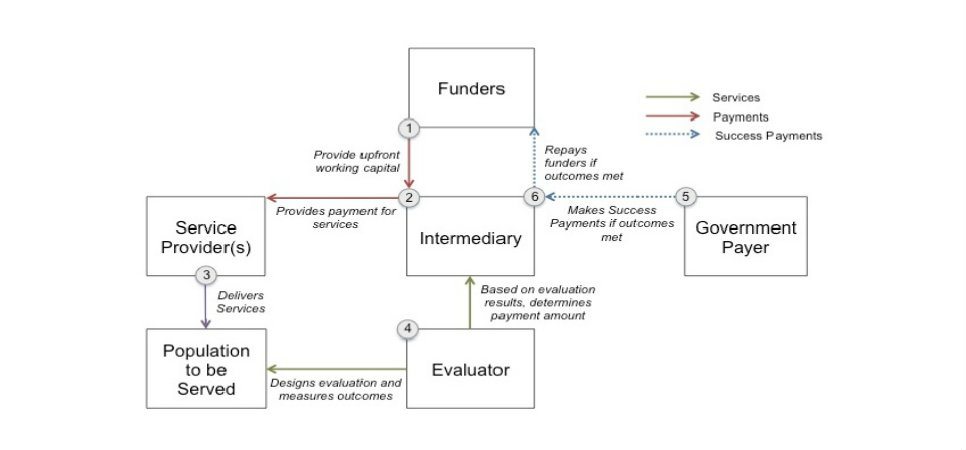
Image developed by Third Sector Capital Partners – Pay for Success Mechanics
Recent Results
The first U.S. SIB contract recently came to a close, providing the market with some valuable lessons. As a government-contracting model, this SIB proved that through creative partnerships the government could experiment without passing the risks on to taxpayers. While the program did not achieve the desired social outcomes—reducing recidivism rates at Rikers Island prison in New York—the city now has a better understanding of this intervention and can make adjustments in the future.
Continuing the 2014 Momentum
Last year, SIBs gained wider attention following two major milestones—the U.S. National Advisory Board (U.S. NAB) publicly launched in June 2014, and in November 2014 it released a report of recommendations for federal policy on impact investing, Private Capital Public Good. Today, SIBs remain an underleveraged tool; however, the Foundation is excited to witness the progress that has grown from the work of the U.S. NAB. Policymakers around the world are seeing the value of bringing the talent, time, philanthropic will and assets from all sectors together to tackle major social problems.
As a member of the U.S. NAB to the G7 Task Force on Impact Investing, Jean Case has been an advocate for the powerful potential and virtues of this “all oars in the water” approach to solving society’s most intractable obstacles. By engaging private investors through both their immense capital assets and talent, we at the Case Foundation believe that governments and service providers will have the support to realize big, measurable gains on the issues communities care about most.
We look forward to more progress and to a future with more innovative government funding for measurable outcomes and impact.